In the world of software development and project management, the term “Agile” is everywhere. But what does it truly mean? For students, IT beginners, and even professionals transitioning into new roles, the landscape of agile methodologies can seem complex. At its core, Agile is not a single, rigid process but a mindset—a philosophy centered on flexibility, collaboration, and delivering value in an iterative way. It’s a powerful departure from traditional, linear project management, and understanding it is crucial for anyone in the tech field.
This guide will demystify Agile, explore its most popular frameworks, and provide a clear study plan for you to begin your journey.
The Agile Mindset: More Than Just a Process
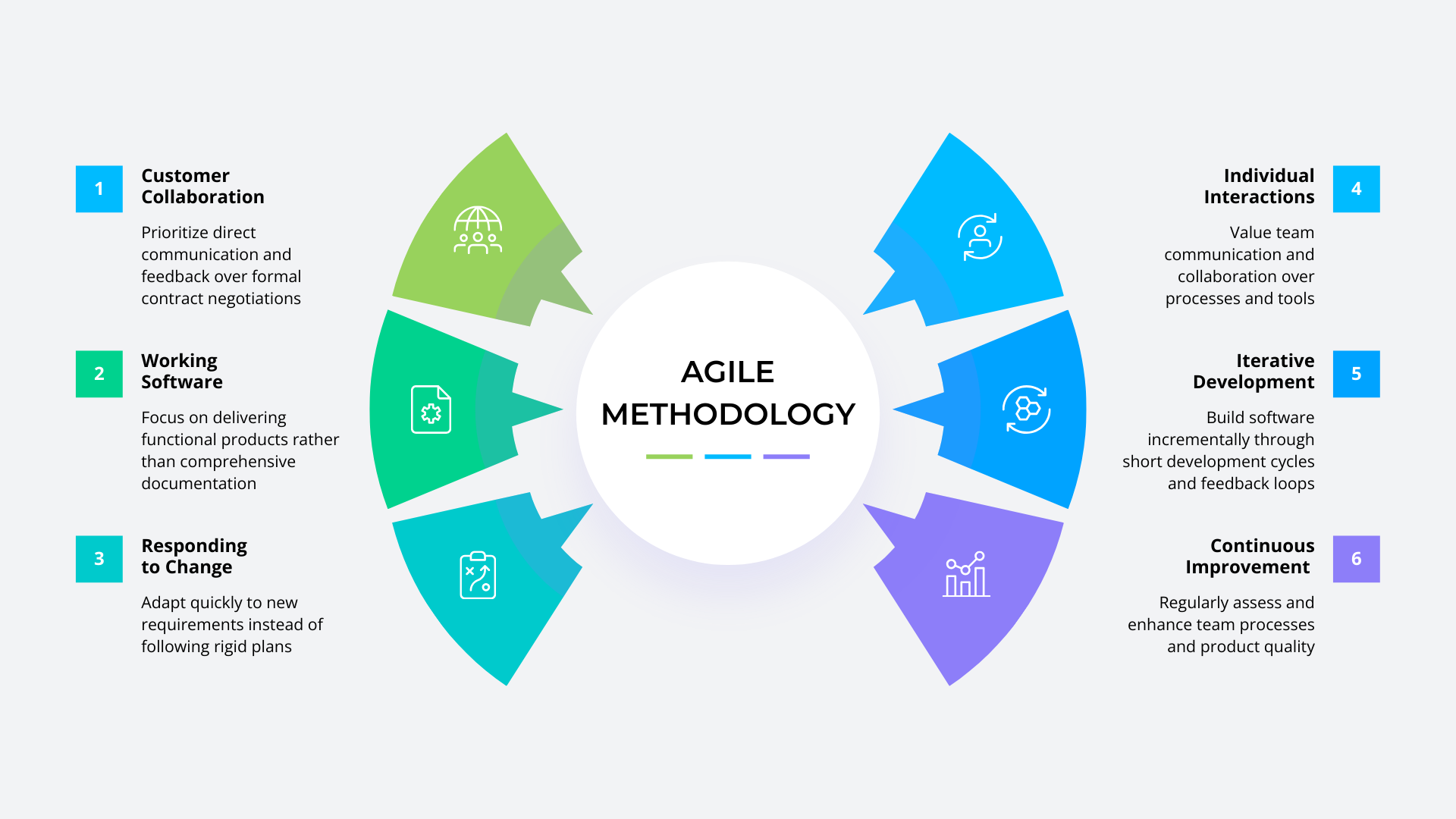
Before diving into specific frameworks, it’s vital to grasp the core principles. The Agile Manifesto, the foundational document for this movement, values four key things:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
This doesn’t mean the items on the right have no value, but that Agile prioritizes the items on the left. This philosophy allows teams to adapt to changing requirements, get feedback early and often, and deliver functional products faster.
Popular Agile Frameworks: Scrum and Kanban
While sharing the same philosophy, different agile methodologies provide unique structures for putting these principles into practice.
Scrum: The Iterative Sprint
Scrum is arguably the most popular Agile framework. It organizes work into fixed-length iterations called “Sprints,” which typically last two to four weeks. Key roles in Scrum include the Product Owner (defines the work), the Scrum Master (facilitates the process), and the Development Team (does the work). Ceremonies like the Daily Stand-up, Sprint Planning, and Retrospective provide a regular cadence for planning, collaboration, and improvement.
Kanban: The Visual Workflow
Kanban is a highly visual and flexible method focused on workflow. Work items are represented as cards on a Kanban board, which is divided into columns representing stages of the process (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done). The primary goal is to manage the flow of work, limit work-in-progress (WIP), and identify bottlenecks. It’s less prescriptive than Scrum and is excellent for teams with continuous delivery needs. For a great digital Kanban board, check out the project management tools we reviewed previously.
Your Agile Study Plan Roadmap for Beginners
Ready to dive deeper? This structured roadmap will guide your learning from foundational concepts to practical application.
Phase 1: Understand the “Why” (1-2 Weeks)
Start with the fundamentals. Don’t just memorize terms; understand the problems Agile solves.
- Read the Agile Manifesto: Read it and its 12 supporting principles. This is the source of truth.
- Study the Scrum Guide: It’s a concise, official document that defines the Scrum framework.
- Watch Introductory Videos: Find beginner-friendly videos on YouTube that explain the concepts of Sprints, User Stories, and Kanban boards.
Phase 2: Deep Dive into a Framework (2-3 Weeks)
Choose one framework—Scrum is a great starting point—and learn its mechanics in detail.
- Take an Online Course: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning have excellent courses on Agile and Scrum fundamentals.
- Learn the Roles and Ceremonies: Understand the responsibilities of each role (Product Owner, Scrum Master) and the purpose of each meeting.
- Explore Kanban Principles: Learn about WIP limits, lead time, and how to read a cumulative flow diagram.
Phase 3: Practical Application and Certification (Ongoing)
Knowledge becomes skill through practice.
- Use Agile for Personal Projects: Create a personal Kanban board on a tool like Trello to manage your study plan or daily tasks.
- Join Agile Communities: Participate in online forums or local meetups to learn from experienced practitioners.
- Consider Certification: Once you have a solid grasp, a certification like the Professional Scrum Master (PSM I) can validate your knowledge and boost your resume.
Start Your Agile Journey Today
Adopting agile methodologies is a journey of continuous learning and improvement. By starting with the core philosophy and following a structured learning path, you can build a strong foundation for a successful career in project management and technology.
What do you think of this study plan? Are there other resources you’d recommend for beginners? Share your thoughts and your own study plans in the comments below!
If this guide helped you, please share it with other students and professionals who are ready to embrace the power of Agile.